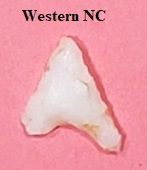
Outline is Representative of Size and Shape:

Name Details:
Identified By: Joffrey L Coe
Named For: Yadkin River in North Carolina
Date Identified: 1964
Type Site: The Doerchuck site, Montgomery County, North Carolina and multiple sites along the Yadkin River
Identified By: Joffrey L Coe
Named For: Yadkin River in North Carolina
Date Identified: 1964
Type Site: The Doerchuck site, Montgomery County, North Carolina and multiple sites along the Yadkin River
Point Validity:
Valid type
Coe was a highly respected and pioneering anthropologist in North Carolina archaeology and a preeminent authority on eastern North American anthropology. This type was named in a professional publication and has many professional references. This is considered a valid type.
Coe was a highly respected and pioneering anthropologist in North Carolina archaeology and a preeminent authority on eastern North American anthropology. This type was named in a professional publication and has many professional references. This is considered a valid type.
Yadkin Triangle
Cluster: <a href="../Clusters/WMTriangle_Cluster.html" target="_blank">Late Woodland to Early Mississippian Triangle Cluster</a> Description of Physical Characteristics and Flaking Pattern:
This is a thin small to medium (1 to 3 inches) triangular point with a flattened cross section. The blade is primarily straight and forms an isosceles triangle (half as wide as the height). The base may range from slightly concaved to deeply concave and may have basal thinning. This point has a random flaking pattern.
Size Measurements:
Total Length - 20 to 90 mm (average 33 to 46 mm), Width - 15 to 43 mm (average 23 to 30 mm), Thickness - 5 to 18 mm (average 6 to 9 mm), Basal Concavity - 1 to 10 mm (average 3 to 5 mm).
Total Length - 20 to 90 mm (average 33 to 46 mm), Width - 15 to 43 mm (average 23 to 30 mm), Thickness - 5 to 18 mm (average 6 to 9 mm), Basal Concavity - 1 to 10 mm (average 3 to 5 mm).
Commonly Utilized Material:
Primarily quartz, but other local materials may be utilized including cherts and jasper
Primarily quartz, but other local materials may be utilized including cherts and jasper
Additional Comments:
Many people consider the Yadkin point and the Levanna point the same type with two different distributions. The Levanna point is found from northern Virginia north and the Yadkin is found from southern Virginia south (roughly). The morphological characteristics of the two points support this argument. However, the dating of the two points becomes problematic. The Levanna point is dated from 700 A.D (Richie, 1971) to as late as 1,350 A.D. (Kinskey, 1972) while the Yadkin point has been dated from 300 B.C. to 800 A.D. (UNC) based on radiocarbon dating of Yadkin ceramics. This dating difference may be due to dating methods used, or could represent a shift in the point usage form the south into the north.
Both the Yadkin and Badin points are large triangular points, but the Yadkin has a higher quality of flaking than is seen in the Badin type points. It has been suggested that the Badin predates the Yadkin type points (UNC).
Many people consider the Yadkin point and the Levanna point the same type with two different distributions. The Levanna point is found from northern Virginia north and the Yadkin is found from southern Virginia south (roughly). The morphological characteristics of the two points support this argument. However, the dating of the two points becomes problematic. The Levanna point is dated from 700 A.D (Richie, 1971) to as late as 1,350 A.D. (Kinskey, 1972) while the Yadkin point has been dated from 300 B.C. to 800 A.D. (UNC) based on radiocarbon dating of Yadkin ceramics. This dating difference may be due to dating methods used, or could represent a shift in the point usage form the south into the north.
Both the Yadkin and Badin points are large triangular points, but the Yadkin has a higher quality of flaking than is seen in the Badin type points. It has been suggested that the Badin predates the Yadkin type points (UNC).
Distribution: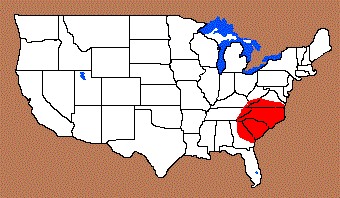
Distribution Comments:
This point is primarily found in the Piedmont region from Virginia to Georgia and into the Blue Ridge regions of those states. This point may be found into the Coastal regions with decreased frequency.
This point is primarily found in the Piedmont region from Virginia to Georgia and into the Blue Ridge regions of those states. This point may be found into the Coastal regions with decreased frequency.
Age / Periods:
Date: 2,300 - 1,500 B.P.
Cultural Period: Middle to Late Woodland
Glacial Period: Roman Warm
Culture:
Date: 2,300 - 1,500 B.P.
Cultural Period: Middle to Late Woodland
Glacial Period: Roman Warm
Culture:
Age Details:
Wood and Ledbetter (1990) found at the Rush site (9FLI64) in northwestern Georgia, Yadkin points were primarily associated with Cartersville ceramics, but were also found in earlier deposits containing Dunlap pottery. (Whatley, 2002).
Wood and Ledbetter (1990) found at the Rush site (9FLI64) in northwestern Georgia, Yadkin points were primarily associated with Cartersville ceramics, but were also found in earlier deposits containing Dunlap pottery. (Whatley, 2002).
Similar Points:
Badin, Camp Creek, Garden Creek, Hamilton Triangle, Fort Ancient, Madison, Levanna, Uwharrie
Badin, Camp Creek, Garden Creek, Hamilton Triangle, Fort Ancient, Madison, Levanna, Uwharrie
Other points in this cluster / Related / Associated Points:
Yadkin Eared
Yadkin Eared